Standardised MP4 material may be sent in real-time or on-demand with an adjustable bitrate using HTTP Dynamic Streaming (HDS). HDS offers tools for incorporating content preparation into preexisting encoding procedures, allowing you to make the most of current caching infrastructures. Video streaming that may be sent on demand or streamed in real-time with HTTP Dynamic Streaming. In this article, we have all about HTTP Dynamic Streaming for your understanding and how beneficial it is for you.
All about Adobe HTTP Dynamic Streaming
The Latest on HTTP Streaming Dynamic: Video Streaming
- Consistent, expandable delivery
For high-volume, high-quality on-demand, and live content delivery, use preexisting cache infrastructures and ordinary HTTP server hardware.
- Incredible scope
Stream premium content to Mac OS, Windows, or Linux desktops and reach the biggest potential audience with content delivery through Adobe® Flash® Player or Adobe AIR® apps.
- Standards for publicly available files
The MP4 fragment format is the standard for variable bitrate distribution and allows for a seamless live streaming experience thanks to its open media and manifest file format guidelines.
- Constantly Changing Bitrate
Determine the client’s bandwidth and processing capability, and then provide them with content chunks that are as tightly packed as you can make them.
- Common HTTP caching framework support
Using standard server hardware and various caching technologies is one way to boost performance while also improving accessibility.
Streaming availability (both live and on-demand)
- Transmit real-time and on-demand video using HTTP.
Adobe Media Server streaming workflows that support Real Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) are used for live delivery, whereas a single processing step is all that’s needed for VOD to get files ready for HTTP Dynamic Streaming with the necessary security measures in place.
- Reporting and monitoring of client activity (with OSMF Omniture plug-in)
You will have the ability to reliably acquire usage data and track playback engagement with the assistance of the OSMF-integrated Omniture® plug-in, therefore opening the path for content monetization and optimization.
- Several Video Coding Schemes
Use high-quality codecs that are supported by the Flash Player (VP6/MP3, H.264/AAC) to encode your material, and then build fragmented files for HTTP Dynamic Streaming distribution either with a single processing step or automatically with real-time packaging.
The joy of playing videos with HTTP Dynamic Streaming
- HD quality
Using either the H.264 or VP6 video codecs, as well as the AAC and MP3 audio codecs, provide high-definition video at a resolution of up to 1080p, with bit rates ranging from 700 kbps all the way up to and above 6Mbps.
- Upgrade from progressive delivery
Experience improved playback capabilities such as interactive seeking, adaptive bitrate streaming, live support, and DVR capability via HTTP connections.
- Framework for playing media that is open source and modifiable
By using Open Source Media Framework, it is possible to quickly and simply add support for HTTP Dynamic Streaming to already existing media players (OSMF).
- DVR capabilities and functions
Support for H.264 stream recording for RTMP and HTTP Dynamic Streaming will allow you to archive live HD broadcasts on the server and provide HD DVR capabilities (such as immediate replay and time shifting), among other features. You may pause a live broadcast or search backwards using this function.
- Multi Camera angles/image in the picture
Enhance the viewing experience with additional elements that add interaction and raise the level of engagement felt by viewers.
- Content protection
Support for encrypted streaming provided by Adobe Access Server.When encrypting your files and implementing a quick play start, you can safeguard your important information while ensuring that viewers have unhindered access. Keep your material under complete control throughout the whole creation process.
Multimedia content delivery through HTTP dynamic streaming
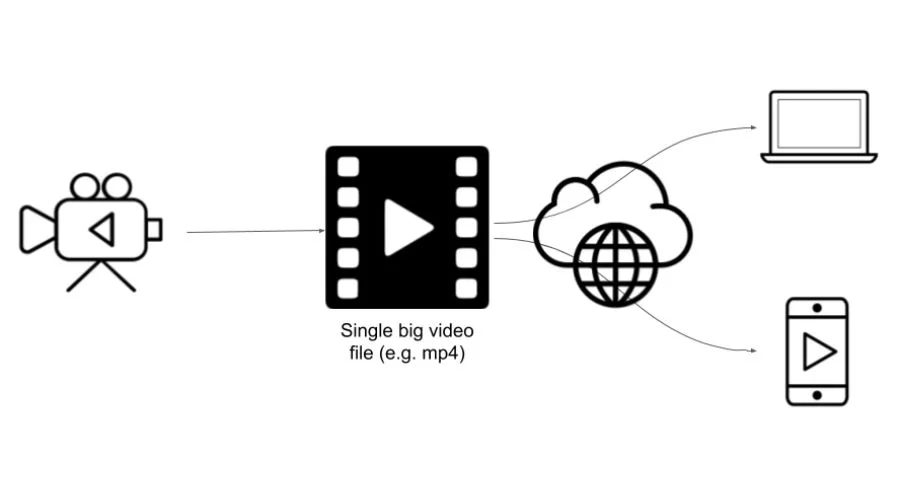
Progressive download is the standard term for HTTP-based content distribution. The data must go sequentially from the server to the client, just as it would in a real file. A client can’t look to an upcoming location until both it and the data before it has completely downloaded.
“Streaming” refers to the process of delivering data using RTMP. By establishing a socket connection with the server (like Adobe Media Server), the client can send data in a constant stream. No matter how much data has been sent, the client may rapidly seek any place in the content.
To bring HTTP streaming to the Flash Platform, Adobe HTTP Dynamic Streaming combines several methods. The HTTP Dynamic Streaming protocol divides up large media files into smaller chunks that may be downloaded in real-time by Flash Player clients. Several parts make up Adobe HTTP Dynamic Streaming, which works in tandem to encapsulate material and transmit it through HTTP to the aforementioned players (Flash Player and AIR). Multi-bitrate streaming, DVR, and Adobe® Flash® AccessTM security are all possible with HTTP Dynamic Streaming.
Conclusion
If you are looking to work with HTTP Dynamic Streaming, this article here has all the information you need to know about HTTP Dynamic Streaming. For more details, please refer to Adobe and the official website of Trending Cult.